| [1] Sun XL, Shi S, He YZ. Guoji Waike Xue Zazhi. 2008;35(10): 681-683.孙晓磊,施森,何延政.糖尿病创面难愈机制的研究进展[J].国际外科学杂志,2008,35(10):681-683.[2] Fang Y. Shanghai Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban. 2009 (12):1403-1406.方勇.创面修复机制及技术研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2009(12):1403-1406.[3] Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1736-1743.[4] Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, et al. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet. 2005;366 (9498):1719-1724.[5] Sen CK, Gordillo GM, Roy S, et al. Human skin wounds: a major and snowballing threat to public health and the economy. Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17(6):763-771.[6] Lima MH, Caricilli AM, de Abreu LL, et al. Topical insulin accelerates wound healing in diabetes by enhancing the AKT and ERK pathways: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36974. [7] Andreassen TT, Oxlund H. The influence of experimental diabetes and insulin treatments on the biochemical properties of rat skin incisional wounds. Acta Chir Scand. 1987;153(7-8): 405-409.[8] Jermendy G. Intensive insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Orv Hetil. 2012;153(38):1487-1493.[9] Wertheimer E, Spravchikov N, Trebicz M, et al. The regulation of skin proliferation and differentiation in the IR null mouse: implications for skin complications of diabetes. Endocrinology. 2001;142(3):1234-1241.[10] Goodson WH 3rd, Hung TK. Studies of wound healing in experimental diabetes mellitus. J Surg Res. 1977;22(3): 221-227.[11] Rezvani O, Shabbak E, Aslani A, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to determine the effects of topical insulin on wound healing. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2009;55(8):22-28.[12] Grotendorst GR, Martin GR, Pencev D, et al. Stimulation of granulation tissue formation by platelet-derived growth factor in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1985;76(6):2323- 2329.[13] Jin YF, Chen SZ. Xiandai Zhongliu Yixue. 2009;17(12): 2274-2276.金玉峰,陈绍宗.胰岛素促进慢性创面愈合的效果及机制[J].现代肿瘤医学,2009,17(12):2274-2276.[14] Szkudelski T. The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res. 2001; 50(6):537-546.[15] Sun N, Yang G, Zhao H, et al. Multidose streptozotocin induction of diabetes in BALB/c mice induces a dominant oxidative macrophage and a conversion of TH1 to TH2 phenotypes during disease progression. Mediators Inflamm. 2005;2005(4):202-209.[16] Ren J, Zeng HF, Li Y, et al. Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2010; 19(5):691-699.任静,曾海峰,栗勇,等.热休克蛋白90促进糖尿病创面愈合的作用研究[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(5):691-699.[17] Zhang Y, Li HY, Dong L, et al. Zhonghua Tangniaobing Zazhi. 2011;3(5):433-435.张毅,李慧颖,董玲,等.链脲佐菌素诱导模拟2型糖尿病动物模型的研究进展[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2011,3(5):433-435.[18] Li WJ, Li B, Kou CG, et al. Jilin Daxue: Yixue Ban. 2004;30(6): 991-993.李文君,李波,寇长贵,等.非胰岛素依赖型糖尿病易感基因定位研究进展[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2004,30(6):991-993.[19] Li CF,Lu Y, Chen XL, et al. Zhongguo Sunshang yu Xiufu Zazhi. 2012;7(1):54-61.李超飞,刘琰,陈雪莲,等.局部应用胰岛素对糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的影响[J].中国损伤与修复杂志,2012,7(1):54-61.[20] Lin TS, Abd Latiff A, Abd Hamid NA, et al. Evaluation of topical tocopherol cream on cutaneous wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:491027. [21] Rodrigues Filho OA, Fazan VP. Streptozotocin induced diabetes as a model of phrenic nerve neuropathy in rats. J Neurosci Methods. 2006;151(2):131-138. [22] Jia WP, Xiang KS. Zhongguo Neifenmi Daixie Zazhi. 2005; 21(3):159-162.贾伟平,项坤三.胰岛β细胞功能评估-从基础到临床[J].中国内分泌代谢杂志,2005,21(3):159-162.[23] Madibally SV, Solomon V, Mitchell RN, et al. Influence of insulin therapy on burn wound healing in rats. J Surg Res. 2003;109(2):92-100.[24] Eldad A, Weinberg A, Breiterman S, et al. Early nonsurgical removal of chemically injured tissue enhances wound healing in partial thickness burns. Burns. 1998;24(2):166-172.[25] Liu Y, Petreaca M, Martins-Green M. Cell and molecular mechanisms of insulin-induced angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(11-12):4492-4504. [26] Apikoglu-Rabus S, Izzettin FV, Turan P, et al. Effect of topical insulin on cutaneous wound healing in rats with or without acute diabetes. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(2):180-185. [27] Teoh SL, Latiff AA, Das S. The effect of topical extract of Momordica charantia (bitter gourd) on wound healing in nondiabetic rats and in rats with diabetes induced by streptozotocin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34(7):815-822. |
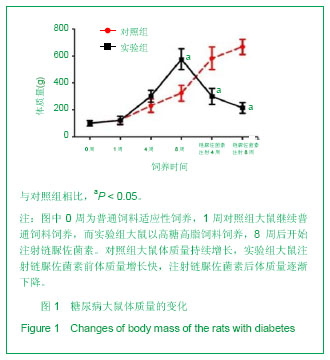
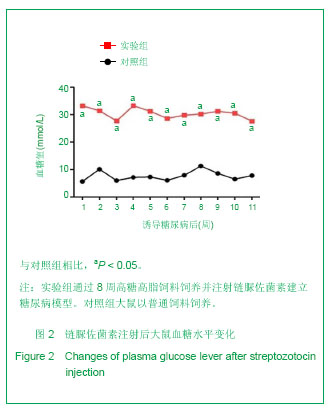
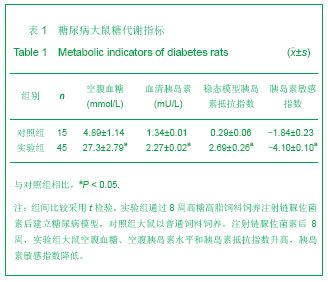
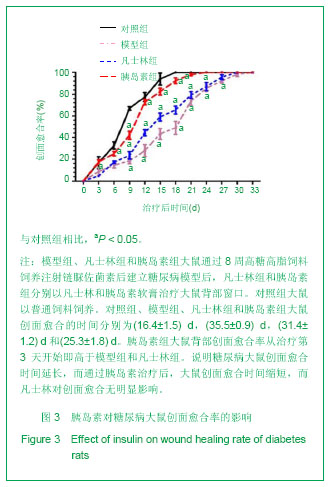
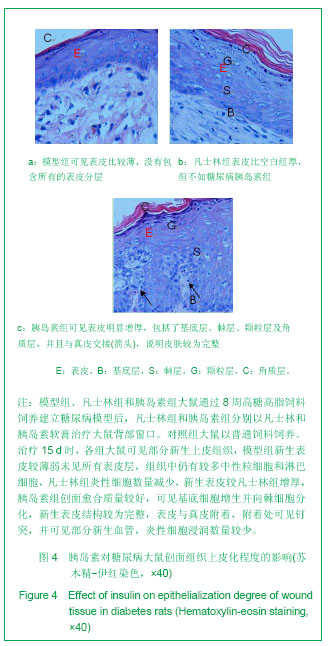

.jpg)
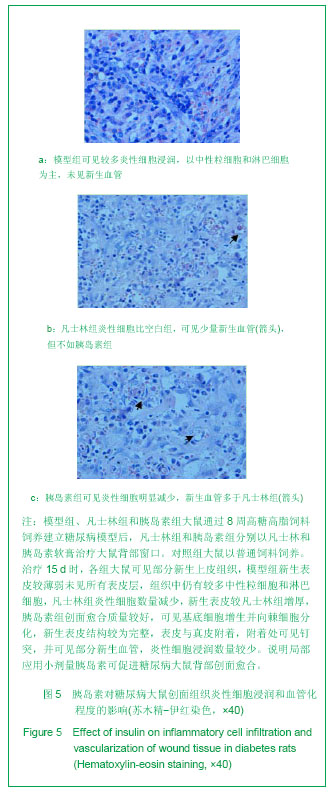
.jpg)